AP3-3
A New Guideway Design for HTS Maglev Vehicle Considering Curve Negotiation
Dec.1 16:40-17:00 (Tokyo Time)
Gebze Technical University, Turkey.1
Sivas Science and Technology University,Turkey.2
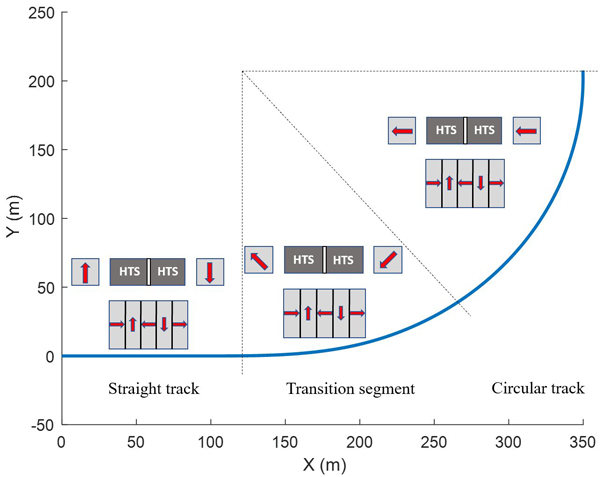
In this paper, we proposed a multi-surface permanent magnet guideway (PMG) design in which polarization of the permanent magnets (PM) changing with track segments. High-temperature superconducting (HTS) maglev systems have been studied by various research groups regarding both experimental and modelling point of view. However, there exists a trade-off between levitation and guidance forces acting on the vehicle, especially in case of high-speed curve negotiation. To overcome this trade-off, we proposed a PMG consisting of three different PM arrangement(Fig.1): the first one for the straight track line to maximize the levitation force, and the second one for the circular track where guiding force is required to be higher to safely negotiate curves. In addition, a transition segment was considered for providing a smoother transition to the previous and next segment. The HTS-PM interaction model was constructed by utilizing H-formulation implemented in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.3. The effectiveness of the proposed track design has been validated through comparisons with Halbach-derived PMG. The hysteretic levitation and guiding force expressions used in the dynamic simulation have been obtained by a polynomial fit to force-displacement curves obtained by the finite element model in COMSOL. According to numerical simulation, an increase of 22.3 % in the levitation force was achieved in the straight track segment when compared to Halbach array PM configuration. Also, an increment up to 33.2 % in the guiding force, with guideway design for circular track, is observed. Moreover, it is shown that the transition segment of PMG plays an important role in smoothing the sudden change in the track’s vertical and lateral stiffness values. Finally, the proposed approach can be effective for the redesigning the PMG for the high-speed operation of a Maglev system.
Keywords: High-temperature superconductors, Maglev System, H-formulation, PM guideway