ED2-7
Si waveguide-integrated SSPD with arrayed waveguide grating
Dec.1 19:45-20:00 (Tokyo Time)
Kitami Institute of Technology, Kitami, Hokkaido, Japan1
NTT Device Technology Labs, NTT Corporation, Atsugi, Kanagawa, Japan2
NTT Nanophotonics Center, NTT Corporation, Atsugi, Kanagawa, Japan3
Monolithic integration of superconducting nanowire single photon detector (SSPD) and optical circuits has recently received attention in quantum photonic information technology. However, many optical components are supposed to use at room temperature, therefore it is not clear which part of optical component should be integrated with SSPD and be cooling. In this research, we study the characteristics of Si waveguide-integrated SSPD with room temperature (rt) arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) and that with cooled AWG.
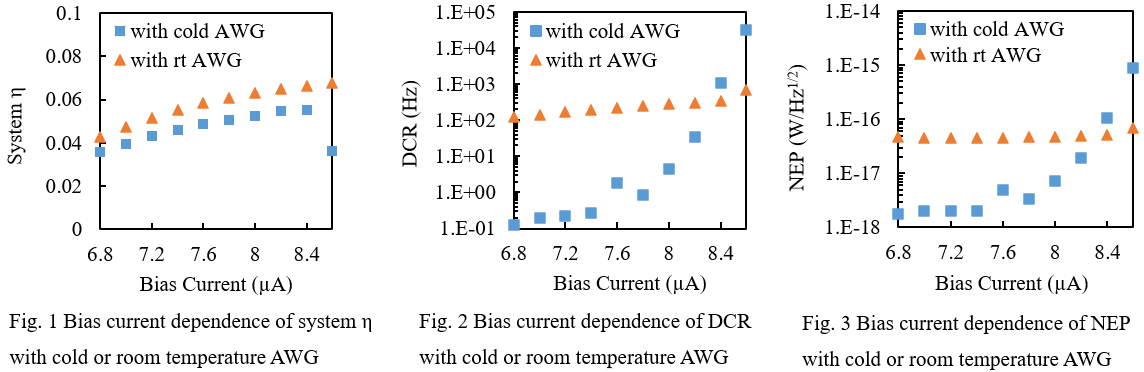
Fig. 1 shows the bias current dependence of system detection efficiency (System η) with cold or rt AWG. System η is similar value in both cases. Fig. 2 shows the bias current dependence of system dark count rate (DCR) with cold or rt AWG. DCR is reduced to 1/100 with cold AWG compared to with rt AWG. This indicates that the cold AWG blocks the room temperature blackbody radiation passing through the optical fiber. Fig. 3 shows bias current dependence of noise equivalent power (NEP) with cold or rt AWG. NEP improves 20 times, from 4.6×10-17 to 2.0×10-18 W/Hz1/2, with cold AWG compared to with rt AWG. These experimental results indicate that monolithic integration of waveguide integrated SSPD and AWG has advantages improving device performances as well as miniaturizing devices.
Keywords: SSPD, SNSPD, AWG