WB4-1
Critical Current Measurement of Commercial REBCO Coated Conductors under Pulsed High Magnetic Field
Dec.2 08:40-08:55 (Tokyo Time)
Department of Electrical Engineering, Nagoya University, Japan1
Center for Advanced High Magnetic Field Science, Graduate School of Science, Osaka University, Japan2
Institute for Solid State Physics, The University of Tokyo, Japan3
A high and steady magnetic field is required for applications such as NMR that requires a long-term and precise measurements. The highest DC field has been realized by a hybrid magnet which combines a resistive and a superconducting one. Recently, a 45T-class all superconducting magnet is realized by using REBCO tapes for the innermost coil [1]. Further development of high field DC magnets requires the measurement of the critical current density Jc in the REBCO tapes in high fields. However, the Jc data is still insufficient. In this study, we have developed a method to investigate the Jc in the REBCO tapes in a pulsed magnetic field of up to 50 T.
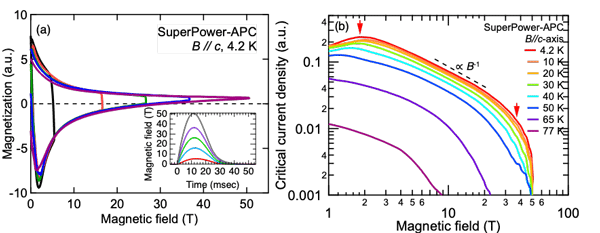
REBCO tapes with artificial pinning centers manufactured by SuperPower Inc. and Fujikura Ltd. were cut into circles with ~2 mm in diameter, and 8-20 pieces of them were stacked together. High field magnetization measurement was performed in a pulsed magnetic field of up to 50 T and at temperatures from 4.2 K to 77 K using a non-destructive pulsed magnet with a pulse duration of 30 ms at the Center for Advanced High Magnetic Field Science (AHMF), Osaka Univ., as shown in the inset of Fig. 1(a). The Jc was calculated using the Bean model.
Figures 1(a) and 1(b) show the field dependences of the magnetization and the Jc in arbitrary units, respectively. Jc is reliable in the field range between 2 T and 40 T because it was calculated from the major loop of magnetization with the same magnetic field ramping rate, as indicated by the arrows in Fig. 1 (b).The power of the field dependence of Jc was ~-1. Since the field ramping rate was up to ~5 kT/s, the electric field in the tapes is estimated as the order of ~1 V/m which is 10,000 times larger than the transport measurements. We will compare the results of Jc in pulsed fields with those of the transport and the magnetization measurement in steady magnetic fields.
This work was partly supported by JST-A-STEP, JSPS(20K15217), and collaboration research with the AHMF through the High Magnetic Field Collaboratory.
References
[1] S. Hahn et. al., Nature 570, 496-499 (2019).
Fig. 1 Field dependences of (a) magnetization and (b) Jc in the REBCO tapes from SuperPower Inc.
Keywords: REBCO coated conductors, Critical current, Pulsed high magnetic field, Magnetization