WB-1-6
Applicability of flux-free hybrid welding to coil-to-coil REBCO CC joints
11:30-11:45 28/11/2023
*Hyung-Seop Shin and Arman Ray Nisay
Andong Nationa University, 1375 Gyeongdong-Ro, Andong, 36729 South Korea
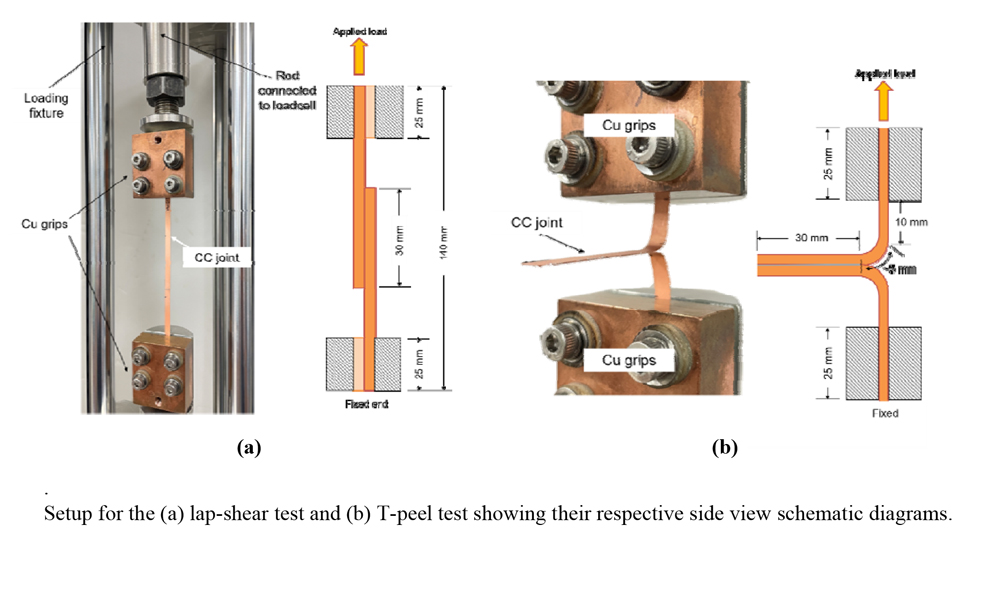
Joining multiple lengths of REBCO coated conductor (CC) tapes is indispensable in fabricating superconducting devices due to the challenge of achieving uniform current transport properties over several kilometers of CC tapes. The authors have established ultrasonic welding (UW) to join differently stabilized and processed CC tapes with superior joint characteristics and electromechanical properties than the conventional soldered joints. Further improvement in the joint characteristics of UW CC joints can be achieved through hybrid welding (HW), a combination of UW and soldering processes, which can compensate for the incomplete connections and presence of voids due to the tool geometry limitations of UW. Moreover, the flux-free HW was established for joining REBCO CC tapes to minimize the corrosion on the joint after a long-term and repeated operation of superconducting devices due to the solder flux residues. The results indicated that the flux-free HW CC lap joints exhibited similar joint resistance (_R_j), joint strength, and electromechanical properties to the cases of with flux and conventional soldered CC joints. However, in the fabrication of coil windings, butt- or bridge-joints are typically used joint structures for connecting stacked CC coils although having higher _R_j than lap-joints. This study adopted the flux-free HW method to fabricate butt- and bridge joints intended for use in coil-to-coil applications. The joint characteristics and electromechanical properties under double-bending were evaluated for each joint structure at 77 K. These findings contribute to developing reliable and high-performance joining of REBCO CC tapes for superconducting devices. Moreover, the flux-free HW CC joints offer the advantages of easy and rapid fabrication without the potential corrosion concerns associated with the solder flux application.
Shin H S, Jung C H and Nisay A R 2020 Joint characteristics of ultrasonic welded CC bridge joints for HTS coil applications Supercond. Sci. Technol. 33 115007
This work was supported by a grant from the National Research Foundation of Korea (2020-R1I1A-3058389) funded by the Ministry of Education (MOE), Republic of Korea. This research was also partially supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. 2022M3I9A1076881).