WB4-4
Evaluation of vortex pinning in strongly pinned YBCO/Y211 superconducting nanocomposite films
Dec.2 09:25-09:40 (Tokyo Time)
Kyushu Institute of Technology, Japan1
Shibaura Institute of Technology, Japan2
CRIEPI, Japan3
Nagoya University, Japan4
Tohoku University, Japan5
YBa2Cu3O7-δ (YBCO) thin films with artificial pinning centers (APCs) have been envisioned for practical applications due to their large critical current density (Jc) over wide range of temperature and applied magnetic field [1]. Apart from exhibiting superior Jc under applied magnetic field, these films also exhibit strong anisotropy which needs to be minimized. Many methods have been successfully employed to improve the critical current properties of YBCO thin films through the incorporation of nanoscale secondary phases into YBCO superconducting film matrix which generate artificial pinning centers (APCs). The incorporated secondary phase nanoinclusions either self-assemble in the form of nanocolumns or nanoparticles depending upon parameters such as lattice misfit and elastic constants of the phases. The nanoparticles of secondary phases are considered to be 3-dimensional artificial pinning centers (3-D APCs) which provide pinning to the quantized vortices irrespective of the orientation of the applied magnetic field which is crucial in minimizing the Jc anisotropy of the YBCO thin films.
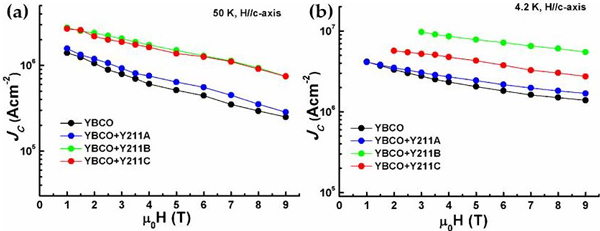
In this paper, the structural, microstructural and transport properties of YBCO thin films incorporating varying concentrations of Y2BaCuO5 (Y211) nanoparticles will be discussed. The effect of systematic incorporation of 3-D APCs on the critical current properties of YBCO thin films on single crystal substrates will be discussed in detail. Our previous study on YBCO films incorporating Y211 nanoparticles has revealed significant reduction of critical current anisotropy at 77 K and 65 K [2]. Fig. 1 shows the variation of critical current density with applied magnetic field for YBCO and YBCO/Y211 nanocomposite films at 50 K and 4.2 K. The geometry and density of these Y211 nanoparticles can further be controlled by varying the deposition conditions in PLD system. The objective of the present study is to investigate systematic variation of 3-D APCs into YBCO films both from the point of view of the vortex pinning properties and also of fundamental understanding of the growth of different species in a thin film under different deposition conditions.
References:
[1] Alok K. Jha and Kaname Matsumoto, Front. Phys. 7, 82 (2019).
[2] Alok K. Jha et al., J. Appl. Phys. 122, 093905 (2017).
Keywords: YBCO, Thin films, APCs, Vortex pinning