WB5-12
Shielding Effect on Flux Trapping in Pulsed-Field Magnetizing for Mg-B Bulk Magnet
Dec.2 16:00-16:15 (Tokyo Time)
Shibaura Institute of Technology1
Niigata University2
Ashikaga University3
IFW Dresden4
Caen University5
University of Lorraine6
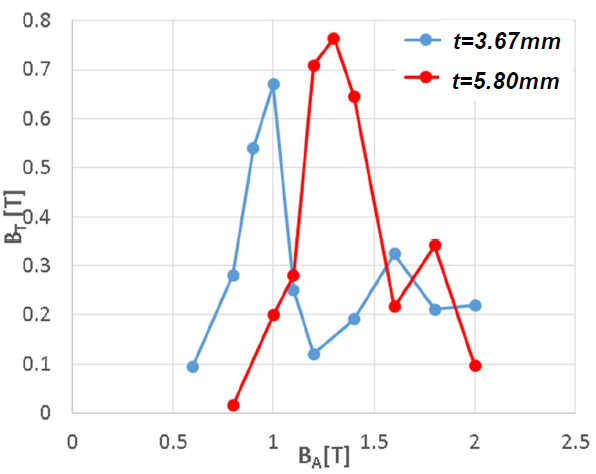
Mg-B superconducting bulk materials are characterized as simple and uniform metallic compounds, and capable of trapping homogeneous field with beautiful conical shapes. Although pulsed-field magnetization technique (PFM) is expected as a cheap and an easy way to activate them, the heat generation due to magnetic flux motion in bulk magnets causes serious degradation of captured fields. It is important to suppress the flux motions during PFM to decrease the heat generation. In this study, authors precisely estimated the flux trapping to the bulk samples, found that the flux-shielding effect related to the sample dimensions. Moreover, the Ti-addition to the bulk sample affected the frequency of flux jump happenings. The magnetic field capturing of 5.0wt%Ti-added samples reached the highest value of 0.76 T, while the starting point of magnetic field invasion into the sample centre shifted from 1.0 T to 1.2 T with increasing sample thickness from 3.67 mm to 5.80 mm. The occurrence of flux jumps was suppressed in 5.0wt%Ti-dopped sample, which means that the heat capacity of the compounds shifted with varying Ti addition, effectively prevented the flux jumps.
Keywords: superconductor, magnesium diboride, pulsed field, magnetic property