WB5-13
Trapped magnetic field characteristics of MgB2 bulk with different additive contents and MgB2 bulk with different types of additives by pulse magnetization
Dec.2 16:15-16:30 (Tokyo Time)
Shibaura Institute of Technology Japan1
Lorraine University France2
IFW Dresden Germany3
Niigata University Japan4
Caen University France5
Ashikaga University Japan6
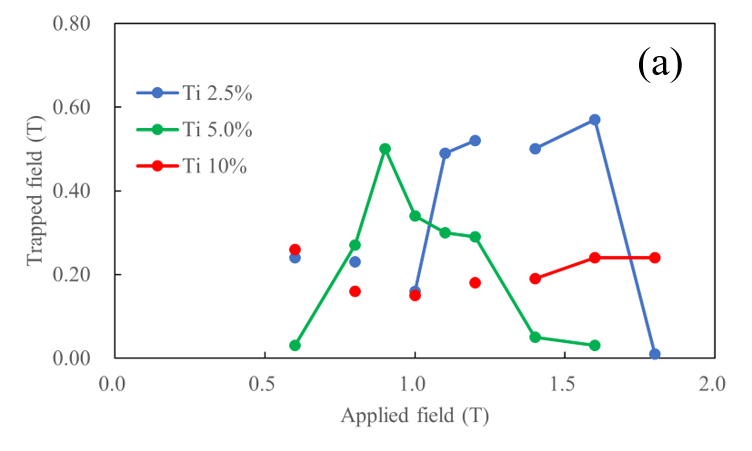
When the MgB2 bulk body is magnetized by the pulse magnetizing method, the MgB2 bulk can take the role of a pseudo permanent magnet. However, it was confirmed that the temperature at which MgB2 is expected to be used is close to the critical temperature (TC) of MgB2 and the specific heat is small, so that the heat generated by the pulse magnetizing method causes flux jump and the trapped magnetic field performance deteriorates. In this study, pulse magnetizing was performed on different samples to verify and consider changes in the trapped magnetic field performance. As the sample, the sample obtained by changing the amount of titanium added was synthesized by uniaxial hot pressing and the sample synthesized by spark plasma sintering (SPS). Figure (a) shows a comparison of the trapped magnetic fields of the samples synthesized by the uniaxial hot press. From Fig. (A), it was shown that the capture magnetic field performance may be improved or deteriorated by the composition ratio of the material, the addition of impurities, and the method of synthesizing the bulk material.
Keywords: Superconductivity, MgB2, Bulk, Pulse magnetization