PC12-6
High temperature superconducting YBa2Cu3O7−x thick films by Inkjet Printing Technology
*Adrià Pacheco1, Diana García1, Lavinia Saltarelli1, Albert Queraltó1, Kapil Gupta1, Jordi Farjas2, Pere Roura2, Susagna Ricart1, Teresa Puig1, Xavier Obradors1
- Institut de Ciències de Materials de Barcelona, CSIC, Campus de la UAB, 08193 Bellaterra, Barcelona, Spain1
- GRMT, Dept. of Physics, Universitat de Girona, Campus Montilivi, Edif. PII, E17071 Girona, Spain2
YBa2Cu3O7−x (YBCO) and other cuprates are very promising materials for its use in the production and distribution of renewable energies. However, the main issues regarding the manufacturing of superconductors are the production costs. Thus, the search for low cost procedures is mandatory. Printed Electronics have emerged on the last decades with strong potential, like Inkjet Printing (IJP) deposition. This is a Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD) method with a wide range of applications, which relies on the deposition of chemical solutions in the form of drops in the range of picolitres (pL) enabling a predefined patterning. Moreover, with the possibility of scaling-up this technology, we look forward for the emergence of such superconductor materials into the market.
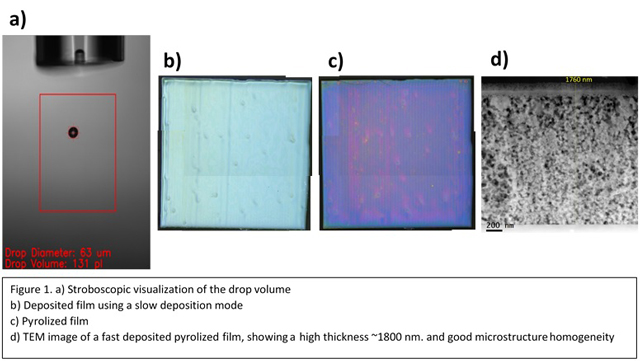
ICMAB-CSIC has developed IJP schemes for CSD TFA-based YBCO layers for long time and reached very relevant results [1, 2]. We could conclude that the TFA-bonds had a very prominent role on the crack-free pyrolysis of the 1 µm YBCO thick films. Here, a novel drop-on-demand IJP deposition methodology for the preparation of flour-free (FF) YBCO films is presented. The advantage relies on the high throughput advantages of the FF precursors if used for TLAG-CSD growth (Transient Liquid Assisted Growth of CSD layers) with ultrafast growth rates of 100 nm/s [3].
The use of different additives, deposition and evaporation strategies were needed to obtain homogenous depositions and pyrolyzed layers with no defects prior to the TLAG growth. Playing with the different characteristics of the fluor-free solutions such its chemical behaviour, use of additives, control of rheology and concentration (mol/L) it was possible to enhance the thickness of the films using such a printing technology while reducing time-consuming processes. The rheological properties of the solution and its thermogravimetric analysis, such as the decomposition pathways of the precursors but also the identification of stress-relief mechanisms, have been analysed using advanced in-situ characterization techniques in order to achieve defect-free homogenous films. By selecting the appropriate actuating wave, drop volume, grid patterning and substrate temperature, homogenous crack-free 1 µm YBCO thick films are obtained in one single deposition, confirmed by TEM analysis. The structural and superconducting properties of the layers are also evaluated, achieving good performances for being compatible with the TLAG method.
[1] B. Villarejo, et al, J. Mater. Chem. C, 8, 10266 (2020)
[2] C. Pop, et al SUST 32, 015004 (2019)
[3] L. Soler, et al, Nat. Comm 11, 344 (2020)
Keywords: Fluor-Free, TLAG, Inkjet Printing, YBCO