WB12-1
Evaluation of Critical Current Characteristics with Contact Resistance and Angle of Superconducting Wire by using FEM
*Yuxuan Zhong1, Edmund S Otabe1, Tomoyuki Akasaka1, Atsushi Ishihara2, Masaru Tomita2
- Kyushu Institute of Technology, Fukuoka, Japan1
- Railway Technical Research Institute, Tokyo, Japan2
Superconducting wires can be connected with high precision at the laboratory level. However, the misalignment (angle) will occur in practical use. At the railway site, it is assumed that some degree of joint misalignment (angle) will occur because the joints will be performed outdoors during the limited time from the last train to the first train. In addition, the joint will be angled due to the deviation of the wire pitch, since the superconducting wire is wound spirally in the superconducting cable.
In this study, in order to clarify the electrical properties of superconducting wires connection with misalignment angle, it is numerically simulated using the finite element method (FEM) (the simulation tools are JMAG-Designer 18.0®), then the electrical properties were evaluated.
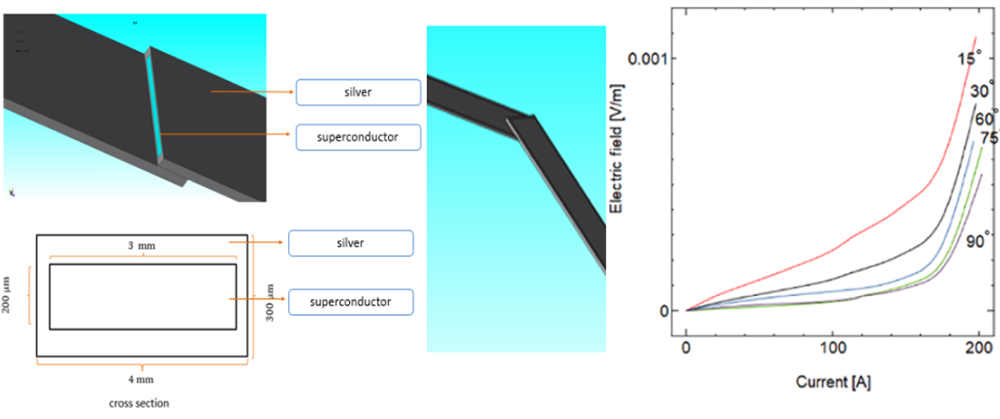
We used a 200μm thick Bi-2223 superconducting layer and silver cover surround it. Total thickness is 300μm. These superconducting wires are jointed together with the angle from 0 to 90°for current density simulation as shown in Figs. 1 and 2. The resistivity of silver at 77.3 K is 1.0×10^-9 Ω/m . The electric filed induced between the both terminals as a function of transport current was numerically calculated. Magnetic field dependence of the critical current density is based on the experimental results of (Bi,Pb)2Sr2Ca2Cu2Oy.
Fig. 3 shows the - characteristics of the superconducting tapes with the angle changes from 15°to . When the electric field equal to 100 µV/m, the current is defined as the critical current. It is found that the critical current increases as the angle increases, since the overlap area increases as increasing the angle.
Fig. 1 Superconducting tape and its cross section.
Fig. 2 Model of the tapes with misalignment angle.
Fig. 3 E-J characteristics of the superconducting tapes with various angle.
Keywords: Critical current density, Angle dependence in superconducting tape