WB4-3
Microstructure and macroscopic superconducting properties of Bulk EuBCO with and without holes
*Veronika Kuchárová1, Pavel Diko1, Daniela Volochová1, Michal Lojka2,3, Tomáš Hlásek2, Vladimír Plecháček2
- Institute of Experimental Physics, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Watsonova 47, 04001 Kosice, Slovakia1
- CAN Superconductors, Ringhofferova 66, 251 68 Kamenice, Czech Republic2
- Faculty of Chemical Technology, University of Chemistry and Technology, Technicka 5, 166 28 Prague 6, Czech Republic3
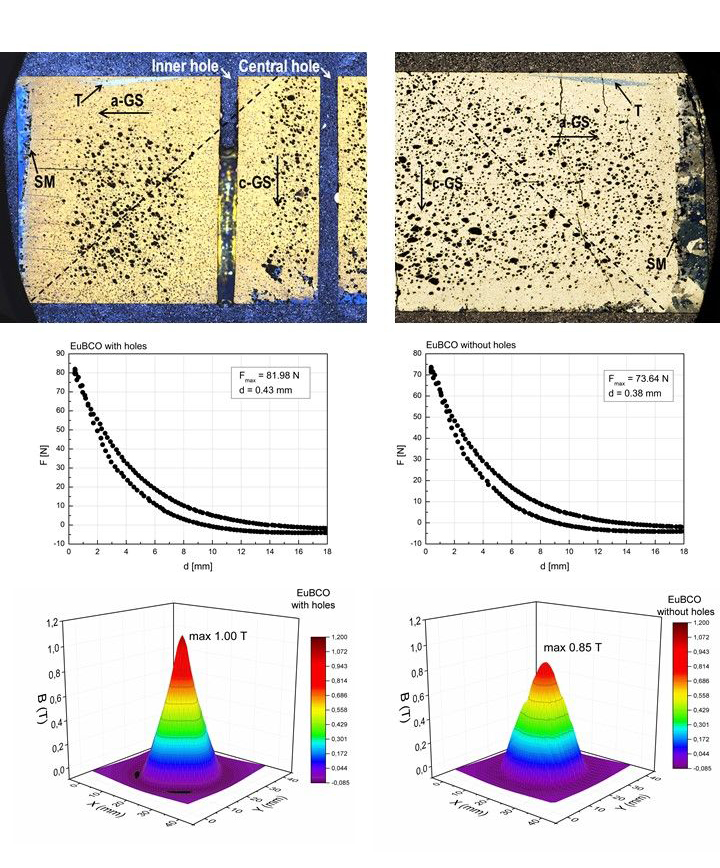
Two EuBCO bulk single-grain superconductors were prepared. Both grew by top-seeded melt-grow process. Sample with holes as well as sample without holes were investigated by microstructural analysis. The volume fraction of Eu211 particles was higher in the a-growth sectors thus the a-growth sectors have better pinning of the magnetic flux lines and consequently a higher critical current density. Porosity of the a-growth sectors was lower in the sample with holes so it can generate higher supercurrents than porous a-growth sectors in the sample without holes. Supercurrent can be further reduced in areas with pores by higher density of a/c-oxygenation cracks present in these areas. The a/b-oxygenation cracks present along the holes in the non-porous areas reduce the supercurrent only minimally. Measurements of levitation force and trapped magnetic field at 77 K showed slightly higher values for the sample with holes despite the higher reduction of the cross-section of the sample by holes and pores. The lower porosity of the a-growth sector with better pinning and the lower density of the of a/c-oxygenation cracks in non-porous areas along the holes could explain this behaviour (Fig. 1).
Figure 1 Microstructure, levitation force and trapped field of sample without holes (left side) and with holes (right side)
Acknowledgement: This work was accomplished within the framework of the projects: Research Centre of Advanced Materials and Technologies for Recent and Future Applications “PROMATECH” (ITMS 26220220186), APVV-17-0625 and VEGA No. 2/0044/19.
Keywords: EuBCO, microstructure, levitation force, trapped field